Woodworking Basic Tool Kit For Beginners – Part 1: Measuring Tools
Measuring Tools:
Some of us might live by the motto: “Measure twice, cut once and force it if it doesn’t fit!” Eventually you will need the correct woodworking measuring tools to make your projects square and professional looking. Here is a brief guide to some basic measuring tools and an explanation of their purpose/function. You are welcome to comment and add on to the list if you like.
Steel Rule:
The steel rule is a basic measuring tool. When used correctly, a good steel rule is a surprisingly accurate measuring device. Some people confuse rules and scales. A scale is a measuring device used by architects and engineers that assists them in making drawings to a scale other than full size.

Machinist Square:
A machinist square, ideal for tool setup and for marking crosscuts precisely, a machinist square slips easily into an apron pocket. Good thing, too, because you’ll reach for this more often than you might think.

Combination square:
A combination square is a tool used for multiple purposes in woodworking, stone masonry and metalworking. It is composed of a ruled blade and one or more interchangeable heads that may be affixed to it. The most common head is the standard or square head which is used to lay out or check right and 45° angles.[1] Invented in 1883 by Laroy S. Starrett,[2] the combination square continues to be a commonplace tool in home workshops, construction jobsites and metalworking.

Sliding bevel:
A sliding T bevel, also known as a bevel gauge or false square is an adjustable gauge for setting and transferring angles. The handle is usually made of wood or plastic and is connected to a metal blade with a thumbscrew or wing nut.

Marking gauge:
A marking gauge, also known as a scratch gauge, is used in woodworking and metalworking to mark out lines for cutting or other operations. The purpose of the gauge is to scribe a line parallel to a reference edge or surface. It is used in joinery and sheetmetal operations.

Framing square:
Also known as a steel square, the Johnson framing square is a handy tool for carpentry. Its uses extend into framing and laying rafters and stairs. It can also be used as a straight-edge, finding and establishing right angles and marking cut-off work on widestock.

Tape Measure:
A tape measure or measuring tape is a flexible ruler. It consists of a ribbon of cloth, plastic, fibre glass, or metal strip with linear-measurement markings. It is a common measuring tool. Its design allows for a measure of great length to be easily carried in pocket or toolkit and permits one to measure around curves or corners.

Folding Rule:
Folding rules, sometimes called zig-zag rules or jointed rules, are a series of two or more smaller rule strips joined with hinges. These rules can be folded together to be carried easily, or used in confined spaces.

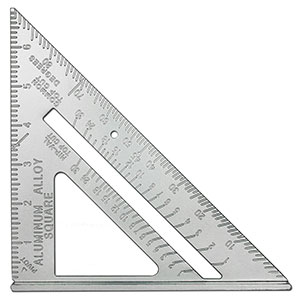
Speed Square:
A Speed Square (rafter square, rafter angle square, triangle square) is a triangular-shaped, carpenters’ marking out tool manufactured and sold by Swanson Tool Co., Inc. The Speed Square combines some of the most common functions of the combination square, try square, and framing square into one.
Compass:
A compass, this simple and inexpensive device can divide almost anything into precise and equal sections, construct complex polygons and find the precise settings for making miters on any angle. Most woodworkers own or have access to this incredibly powerful layout, design and problem-solving tool.

Scratch awl:
A scratch awl is a woodworking layout and point-making tool. It is used to scribe a line to be followed by a hand saw or chisel when making woodworking joints and other operations. The scratch awl is basically a steel spike with its tip sharpened to a fine point.

Vernier:
A vernier scale is a visual aid that allows the user to measure more precisely than could be done unaided when reading a uniformly divided straight or circular measurement scale. It is a scale that indicates where the measurement lies in between two of the graduations on the main scale.

Digital Depth Gauge:
The digital depth gauge is an instrument used to measure the depth, width and height of tooling in stationary machines.


Comments
Add comment